An Example of a Retailerã¢â‚¬â„¢s Regularly Reviewing Operations Is the _____
Office I: What is an information system?
Affiliate 4: Data and Databases
Upon successful completion of this chapter, you volition be able to:
- Describe the differences between data, information, and noesis;
- Describe why database technology must exist used for data resource direction;
- Ascertain the term database and identify the steps to creating one;
- Describe the role of a database management organization;
- Describe the characteristics of a data warehouse; and
- Define data mining and describe its role in an system.
Introduction
You lot take already been introduced to the first ii components of information systems: hardware and software. Still, those two components by themselves do non brand a computer useful. Imagine if you turned on a computer, started the discussion processor, but could non save a document. Imagine if you lot opened a music actor but there was no music to play. Imagine opening a spider web browser but there were no web pages. Without information, hardware and software are not very useful! Data is the third component of an data organisation.
Data, Information, and Knowledge
There have been many definitions and theories nearly data, data, and cognition. The three terms are oftentimes used interchangeably, although they are distinct in nature. We define and illustrate the three terms from the perspective of information systems.
 Data are the raw facts, and may exist devoid of context or intent. For example, a sales guild of computers is a piece of data. Data can be quantitative or qualitative. Quantitative data is numeric, the result of a measurement, count, or some other mathematical calculation. Qualitative data is descriptive. "Ruby Reddish," the color of a 2013 Ford Focus, is an instance of qualitative data. A number tin be qualitative as well: if I tell you my favorite number is v, that is qualitative data because it is descriptive, not the result of a measurement or mathematical adding.
Data are the raw facts, and may exist devoid of context or intent. For example, a sales guild of computers is a piece of data. Data can be quantitative or qualitative. Quantitative data is numeric, the result of a measurement, count, or some other mathematical calculation. Qualitative data is descriptive. "Ruby Reddish," the color of a 2013 Ford Focus, is an instance of qualitative data. A number tin be qualitative as well: if I tell you my favorite number is v, that is qualitative data because it is descriptive, not the result of a measurement or mathematical adding.
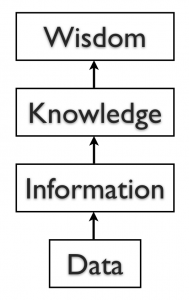
Information is processed data that possess context, relevance, and purpose. For case, monthly sales calculated from the collected daily sales data for the past yr are information. Information typically involves the manipulation of raw information to obtain an indication of magnitude, trends, in patterns in the information for a purpose.
Cognition in a certain area is human beliefs or perceptions about relationships amid facts or concepts relevant to that expanse. For example, the conceived human relationship between the quality of goods and the sales is knowledge. Noesis tin can be viewed as information that facilitates activity.
Once we have put our data into context, aggregated and analyzed it, we can employ it to make decisions for our organisation. We can say that this consumption of data produces knowledge. This noesis can exist used to make decisions, set policies, and even spark innovation.
Explicit noesis typically refers to cognition that can be expressed into words or numbers. In contrast, tacit knowledge includes insights and intuitions, and is hard to transfer to another person by ways of simple communications.
Evidently, when information or explicit knowledge is captured and stored in computer, it would become data if the context or intent is devoid.
The final step upward the information ladder is the pace from knowledge (knowing a lot about a topic) to wisdom. We tin can say that someone has wisdom when they can combine their knowledge and feel to produce a deeper understanding of a topic. It oftentimes takes many years to develop wisdom on a detail topic, and requires patience.
Big Data
Almost all software programs require data to do anything useful. For example, if you are editing a document in a word processor such every bit Microsoft Discussion, the certificate you are working on is the data. The discussion-processing software can manipulate the data: create a new document, duplicate a document, or change a document. Some other examples of data are: an MP3 music file, a video file, a spreadsheet, a web page, a social media postal service, and an e-book.
Recently, large data has been capturing the attention of all types of organizations. The term refers to such massively large data sets that conventional data processing technologies do not accept sufficient power to analyze them. For case, Walmart must process millions client transactions every hour across the world. Storing and analyzing that much data is beyond the ability of traditional information management tools. Understanding and developing the best tools and techniques to manage and analyze these large data sets are a problem that governments and businesses akin are trying to solve.
Databases
The goal of many data systems is to transform data into information in lodge to generate knowledge that can be used for conclusion making. In guild to practise this, the organisation must be able to take data, allow the user to put the information into context, and provide tools for assemblage and analysis. A database is designed for but such a purpose.
Why Databases?
Data is a valuable resources in the organization. However, many people practise not know much about database technology, but utilise non-database tools, such as Excel spreadsheet or Discussion document, to store and manipulate business organization data, or use poorly designed databases for concern processes. Every bit a result, the information are redundant, inconsistent, inaccurate, and corrupted. For a modest data set, the use of non-database tools such as spreadsheet may not cause serious problem. However, for a big organisation, corrupted data could atomic number 82 to serious errors and destructive consequences. The common defects in data resource management are explained every bit follows.
(1) No control of redundant information
People often keep redundant data for convenience. Redundant data could brand the data fix inconsistent. We use an illustrative example to explain why redundant information are harmful. Suppose the registrar'southward office has two divide files that store student data: 1 is the registered pupil roster which records all students who have registered and paid the tuition, and the other is student grade roster which records all students who have received grades.
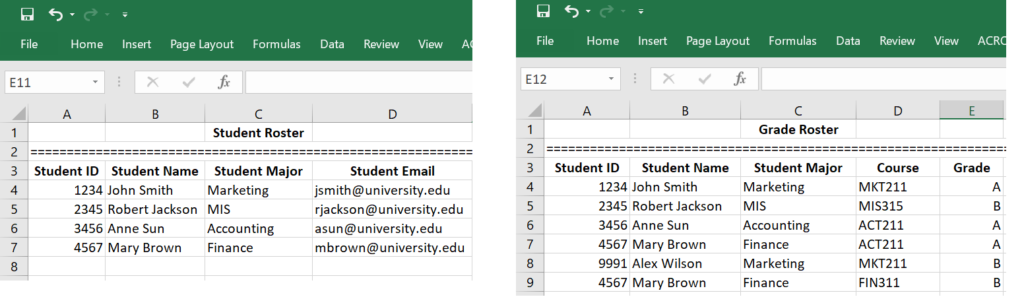
As you can see from the two spreadsheets, this data management arrangement has problems. The fact that "Student 4567 is Mary Chocolate-brown, and her major is Finance" is stored more than in one case. Such occurrences are called data redundancy. Redundant data oft brand data access convenient, but can exist harmful. For example, if Mary Brown changes her proper name or her major, then all her names and major stored in the system must be inverse altogether. For small data systems, such a trouble looks trivial. However, when the information system is huge, making changes to all redundant data is difficult if not incommunicable. As a result of information redundancy, the entire data set tin can be corrupted.
(ii) Violation of information integrity
Data integrity means consistency among the stored data. Nosotros use the to a higher place illustrative example to explain the concept of data integrity and how data integrity tin can be violated if the data system is flawed. You tin can find that Alex Wilson received a grade in MKT211; however, you can't find Alex Wilson in the student roster. That is, the 2 rosters are not consequent. Suppose we accept a information integrity command to enforce the rules, say, "no student can receive a grade unless she/he has registered and paid tuition", then such a violation of information integrity can never happen.
(3) Relying on homo memory to store and to search needed data
The tertiary common mistake in data resource management is the over use of human memory for data search. A homo tin can remember what data are stored and where the data are stored, but tin can also make mistakes. If a slice of information is stored in an un-remembered place, it has actually been lost. Equally a outcome of relying on human retentivity to store and to search needed data, the entire data fix eventually becomes disorganized.
To avoid the above common flaws in information resources direction, database engineering must exist applied. A database is an organized collection of related information. Information technology is an organized collection, because in a database, all information is described and associated with other data. For the purposes of this text, we will only consider computerized databases.
Though non good for replacing databases, spreadsheets can exist ideal tools for analyzing the information stored in a database. A spreadsheet parcel tin be continued to a specific table or query in a database and used to create charts or perform analysis on that information.
Data Models and Relational Databases
Databases can be organized in many different ways by using unlike models. The data model of a database is the logical structure of data items and their relationships. There accept been several data models. Since the 1980s, the relational data model has been popularized. Currently, relational database systems are usually used in business organizations with few exceptions. A relational data model is piece of cake to understand and use.
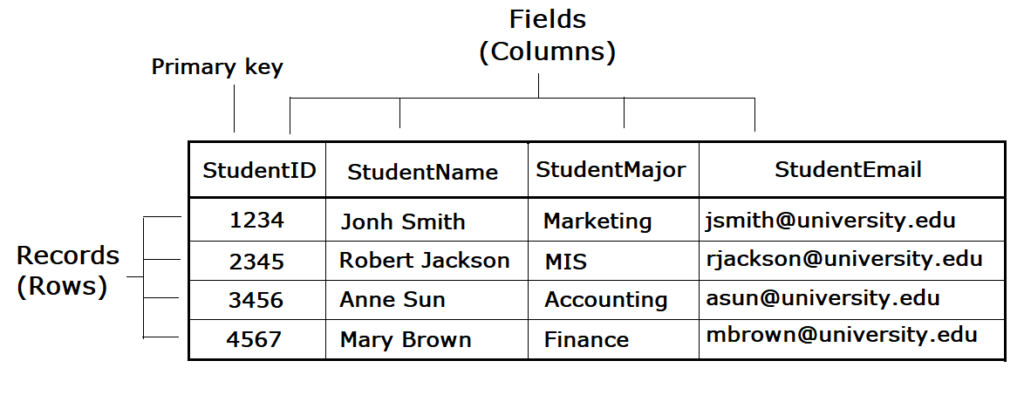
In a relational database, data is organized into tables (or relations). Each tabular array has a fix of fields which define the construction of the data stored in the table. A record is ane instance of a gear up of fields in a table. To visualize this, call up of the records as the rows (or tuple) of the table and the fields as the columns of the table.
In the example below, we take a tabular array of educatee data, with each row representing a student record , and each column representing one filed of the educatee record. A special filed or a combination of fields that determines the unique tape is called primary cardinal (or key). A key is ordinarily the unique identification number of the records.
Designing a Database
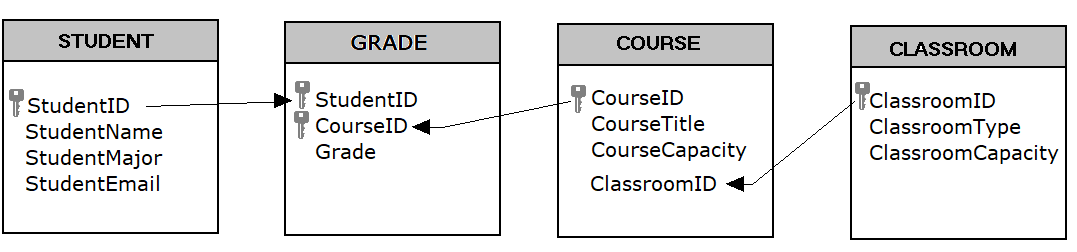
Suppose a university wants to create a School Database to track data. After interviewing several people, the design team learns that the goal of implementing the arrangement is to give improve insight into students' performance and bookish resource. From this, the team decides that the organization must keep track of the students, their grades, courses, and classrooms. Using this information, the pattern squad determines that the following tables need to be created:
- STUDENT: student proper name, major, and electronic mail.
- COURSE: course title, enrollment capacity.
- Class: this table will correlate Pupil with Class, allowing u.s.a. to take any given student to enroll multiple courses and to receive a course for each form.
- CLASSROOM: classroom location, classroom type, and classroom capacity
Now that the design team has determined which tables to create, they need to define the specific data items that each table will hold. This requires identifying the fields that will be in each table. For example, course title would be one of the fields in the Course table. Finally, since this will be a relational database, every table should have a field in common with at least one other table (in other words, they should have relationships with each other).
A primary key must be selected for each table in a relational database. This key is a unique identifier for each record in the table. For instance, in the STUDENT table, it might be possible to apply the pupil name equally a mode to place a pupil. However, it is more than probable that some students share the same proper name. A pupil'due south e-mail service address might be a good selection for a principal fundamental, since electronic mail addresses are unique. However, a primary key cannot change, so this would mean that if students changed their e-mail accost we would have to remove them from the database and so re-insert them – not an attractive proposition. Our solution is to use student ID equally the chief key of the Educatee table. Nosotros will besides exercise this for the COURSE table and the CLASSROOM table. This solution is quite common and is the reason yous have then many IDs! The primary cardinal of table tin can be only one field, but tin as well be a combination of ii or more fields. For example, the combination of StudentID and CourseID the Grade table tin be the primary fundamental of the Form tabular array, which means that a grade is received by a particular student for a specific course.
The next step of design of database is to identify and make the relationships between the tables so that you tin pull the data together in meaningful ways. A relationship between two tables is implemented by using a foreign key. A strange key is a field in i table that connects to the chief key data in the original table. For case, ClassroomID in the COURSE table is the foreign primal that connects to the primary key ClassroomID in the CLASSROOM table. With this pattern, non only do nosotros have a manner to organize all of the data we need and have successfully related all the table together to encounter the requirements, but have also prevented invalid information from being entered into the database. Yous tin can meet the terminal database design in the figure below:
Normalization
When designing a database, one important concept to understand is normalization. In elementary terms, to normalize a database means to design information technology in a manner that: ane) reduces data redundancy; and 2) ensure data integrity.
In the Schoolhouse Database design, the design team worked to achieve these objectives. For example, to rail grades, a simple (and wrong) solution might accept been to create a Pupil field in the Course tabular array and and so merely list the names of all of the students there. However, this pattern would mean that if a pupil takes two or more courses, so his or her data would have to be entered twice or more times. This ways the data are redundant. Instead, the designers solved this problem by introducing the GRADE tabular array.
In this design, when a student registers into the schoolhouse arrangement earlier taking a course, we first must add the student to the Pupil table, where their ID, proper noun, major, and electronic mail address are entered. Now nosotros will add a new entry to announce that the educatee takes a specific form. This is achieved by calculation a record with the StudentD and the CourseID in the GRADE table. If this pupil takes a second course, nosotros practise not have to duplicate the entry of the student's name, major, and e-mail service; instead, we only demand to make another entry in the GRADE table of the second course's ID and the student'due south ID.
The design of the School database besides makes information technology elementary to modify the design without major modifications to the existing construction. For case, if the pattern squad were asked to add together functionality to the organization to rail instructors who teach the courses, we could easily accomplish this past adding a PROFESSOR table (similar to the Student table) and then adding a new field to the COURSE table to hold the professors' ID.
Information Types
When defining the fields in a database table, we must give each field a data type. For example, the field StudentName is text cord, while EnrollmentCapacity is number. Near modernistic databases allow for several different data types to be stored. Some of the more than mutual information types are listed hither:
- Text: for storing non-numeric information that is brief, mostly under 256 characters. The database designer can identify the maximum length of the text.
- Number: for storing numbers. There are unremarkably a few unlike number types that can be selected, depending on how big the largest number will exist.
- Boolean: a data type with only ii possible values, such as 0 or 1, "true" or "imitation", "aye" or "no".
- Date/Fourth dimension: a special form of the number data blazon that tin be interpreted every bit a number or a time.
- Currency: a special form of the number information type that formats all values with a currency indicator and 2 decimal places.
- Paragraph Text: this data type allows for text longer than 256 characters.
- Object: this data type allows for the storage of data that cannot be entered via keyboard, such as an image or a music file.
There are two important reasons that we must properly define the data blazon of a field. Kickoff, a data type tells the database what functions can be performed with the information. For example, if we wish to perform mathematical functions with one of the fields, we must be sure to tell the database that the field is a number data type. For instance, we tin can subtract the course capacity from the classroom capacity to detect out the number of actress seats available.
The second important reason to ascertain data type is so that the proper amount of storage infinite is allocated for our data. For example, if the StudentName field is defined as a Text(fifty) data type, this means 50 characters are allocated for each name nosotros desire to store. If a pupil's proper noun is longer than 50 characters, the database will truncate it.
Database Direction Systems
To the computer, a database looks like one or more files. In order for the data in the database to be stored, read, inverse, added, or removed, a software programme must admission it. Many software applications accept this ability: iTunes tin read its database to give you a listing of its songs (and play the songs); your mobile-phone software can interact with your list of contacts. But what almost applications to create or manage a database? What software tin can you lot use to create a database, alter a database's construction, or merely do analysis? That is the purpose of a category of software applications called database management systems (DBMS).
DBMS packages generally provide an interface to view and change the design of the database, create queries, and develop reports. Most of these packages are designed to work with a specific type of database, but by and large are compatible with a wide range of databases.
A database that can only exist used by a single user at a time is not going to meet the needs of most organizations. Equally computers have become networked and are now joined worldwide via the Internet, a class of database has emerged that can be accessed past two, ten, or fifty-fifty a million people. These databases are sometimes installed on a single computer to be accessed past a group of people at a unmarried location. Other times, they are installed over several servers worldwide, meant to be accessed by millions. In enterprises the relational DBMS are built and supported by companies such as Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and IBM Db2. The open up-source MySQL is also an enterprise database.
Microsoft Access and Open Office Base are examples of personal database-management systems. These systems are primarily used to develop and analyze single-user databases. These databases are not meant to be shared across a network or the Internet, but are instead installed on a item device and work with a single user at a time. Apache OpenOffice.org Base (see screen shot) can be used to create, modify, and clarify databases in open-database (ODB) format. Microsoft's Access DBMS is used to piece of work with databases in its own Microsoft Access Database format. Both Admission and Base have the power to read and write to other database formats too.
Structured Query Language
Once you have a database designed and loaded with information, how will you lot exercise something useful with it? The principal way to work with a relational database is to apply Structured Query Language, SQL (pronounced "sequel," or simply stated as S-Q-Fifty). Almost all applications that work with databases (such equally database management systems, discussed below) make employ of SQL equally a style to analyze and manipulate relational information. Every bit its name implies, SQL is a language that tin can be used to piece of work with a relational database. From a
simple request for data to a circuitous update functioning, SQL is a mainstay of programmers and database administrators. To give you a taste of what SQL might look like, hither are a couple of examples using our School database:
The following query will retrieve the major of educatee John Smith from the Student table:
SELECT StudentMajor FROM STUDENT WHERE StudentName = 'John Smith';
The post-obit query will list the total number of students in the STUDENT table:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Pupil;
SQL can be embedded in many figurer languages that are used to develop platform-independent web-based applications. An in-depth clarification of how SQL works is beyond the telescopic of this introductory text, merely these examples should requite y'all an idea of the power of using SQL to manipulate relational databases. Many DBMS, such equally Microsoft Admission, let you to use QBE (Query-by-Case), a graphical query tool, to retrieve data though visualized commands. QBE generates SQL for yous, and is easy to utilise. In comparison with SQL, QBE has limited functionalities and is unable to piece of work without the DBMS environment.
Other Types of Databases
The relational database model is the most used database model today. However, many other database models be that provide different strengths than the relational model. The hierarchical database model, popular in the 1960s and 1970s, continued data together in a bureaucracy, allowing for a parent/child relationship betwixt data. The document-axial model allowed for a more unstructured data storage by placing data into "documents" that could then be manipulated.
Peradventure the most interesting new development is the concept of NoSQL (from the phrase "not merely SQL"). NoSQL arose from the need to solve the problem of large-scale databases spread over several servers or even across the globe. For a relational database to work properly, information technology is of import that only one person be able to manipulate a piece of data at a time, a concept known as tape-locking. Just with today's large-calibration databases (think Google and Amazon), this is just not possible. A NoSQL database tin work with data in a looser way, assuasive for a more unstructured environs, communicating changes to the data over fourth dimension to all the servers that are role of the database.
Equally stated earlier, the relational database model does not scale well. The term calibration here refers to a database getting larger and larger, existence distributed on a larger number of computers connected via a network. Some companies are looking to provide big-scale database solutions by moving away from the relational model to other, more than flexible models. For example, Google at present offers the App Engine Datastore, which is based on NoSQL. Developers can use the App Engine Datastore to develop applications that access data from anywhere in the earth. Amazon.com offers several database services for enterprise use, including Amazon RDS, which is a relational database service, and Amazon DynamoDB, a NoSQL enterprise solution.
Sidebar: What Is Metadata?
The term metadata can be understood as "data almost data." Examples of metadata of database are:
- number of records
- data blazon of field
- size of field
- description of field
- default value of field
- rules of use.
When a database is being designed, a "data dictionary" is created to hold the metadata, defining the fields and structure of the database.
Finding Value in Data: Business organization Intelligence
With the ascent of Big Information and a myriad of new tools and techniques at their disposal, businesses are learning how to use data to their advantage. The term business organisation intelligence is used to depict the process that organizations use to accept data they are collecting and analyze it in the hopes of obtaining a competitive reward. Besides using their own information, stored in data warehouses (see below), firms often purchase data from data brokers to get a big-flick understanding of their industries and the economic system. The results of these analyses tin can drive organizational strategies and provide competitive reward.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and information. These graphical representations (such as charts, graphs, and maps) can quickly summarize data in a way that is more than intuitive and can pb to new insights and understandings. Just as a moving picture of a landscape can convey much more than a paragraph of text attempting to depict it, graphical representation of information can quickly brand meaning of big amounts of data. Many times, visualizing data is the first step towards a deeper analysis and understanding of the information nerveless by an system. Examples of information visualization software include Tableau and Google Data Studio.
Information Warehouses
Every bit organizations have begun to utilize databases as the centerpiece of their operations, the need to fully understand and leverage the data they are collecting has get more and more credible. All the same, straight analyzing the data that is needed for day-to-twenty-four hours operations is non a good idea; we practice non desire to tax the operations of the visitor more than than nosotros need to. Further, organizations also desire to clarify data in a historical sense: How does the data we take today compare with the same set of data this time last month, or final yr? From these needs arose the concept of the information warehouse.
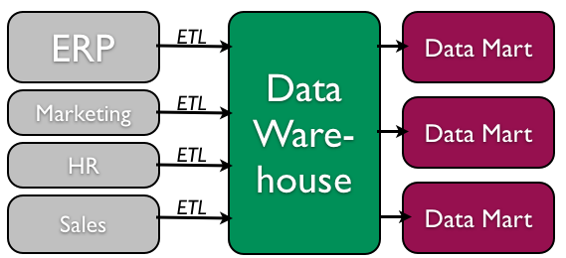
The concept of the data warehouse is simple: extract data from one or more of the organization's databases and load it into the data warehouse (which is itself another database) for storage and analysis. Still, the execution of this concept is not that simple. A information warehouse should be designed so that it meets the following criteria:
- It uses non-operational data. This means that the data warehouse is using a copy of data from the agile databases that the company uses in its twenty-four hour period-to-day operations, so the data warehouse must pull data from the existing databases on a regular, scheduled basis.
- The information is time-variant. This ways that whenever data is loaded into the data warehouse, information technology receives a fourth dimension stamp, which allows for comparisons between different time periods.
- The data is standardized. Because the data in a data warehouse usually comes from several different sources, information technology is possible that the data does not utilise the aforementioned definitions or units. For case, each database uses its own format for dates (e.k., mm/dd/yy, or dd/mm/yy, or yy/mm/dd, etc.). In order for the information warehouse to lucifer upward dates, a standard date format would have to be agreed upon and all information loaded into the data warehouse would have to be converted to apply this standard format. This process is chosen extraction-transformation-load (ETL).
There are two primary schools of idea when designing a data warehouse: bottom-up and top-downwards. The bottom-upwardly approach starts by creating small data warehouses, chosen data marts, to solve specific business problems. As these data marts are created, they can be combined into a larger information warehouse. The top- down arroyo suggests that we should start by creating an enterprise-broad data warehouse and then, as specific concern needs are identified, create smaller data marts from the data warehouse.
Benefits of Data Warehouses
Organizations discover data warehouses quite beneficial for a number of reasons:
- The process of developing a data warehouse forces an arrangement to ameliorate sympathise the data that it is currently collecting and, equally important, what data is not being collected.
- A data warehouse provides a centralized view of all data beingness collected beyond the enterprise and provides a ways for determining data that is inconsistent.
- Once all data is identified as consequent, an organization tin can generate "one version of the truth". This is of import when the company wants to written report consistent statistics nearly itself, such as revenue or number of employees.
- Past having a data warehouse, snapshots of data can be taken over fourth dimension. This creates a historical tape of data, which allows for an analysis of trends.
- A data warehouse provides tools to combine data, which can provide new data and assay.
Data Mining and Machine Learning
Information mining is the process of analyzing data to observe previously unknown and interesting trends, patterns, and associations in club to make decisions. Generally, information mining is achieved through automated means against extremely large information sets, such equally a data warehouse. Some examples of data mining include:
- An assay of sales from a large grocery chain might determine that milk is purchased more frequently the day after it rains in cities with a population of less than 50,000.
- A bank may observe that loan applicants whose bank accounts show particular deposit and withdrawal patterns are not proficient credit risks.
- A baseball team may find that collegiate baseball players with specific statistics in hitting, pitching, and fielding make for more successful major league players.
One information mining method that an system can use to do these analyses is called machine learning. Machine learning is used to clarify data and build models without being explicitly programmed to do so. Ii chief branches of machine learning be: supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
Supervised learning occurs when an organization has data virtually by activity that has occurred and wants to replicate it. For example, if they desire to create a new marketing campaign for a particular product line, they may look at data from past marketing campaigns to see which of their consumers responded most favorably. Once the assay is done, a automobile learning model is created that can be used to identify these new customers. It is called "supervised" learning considering we are directing (supervising) the analysis towards a result (in our instance: consumers who respond favorably). Supervised learning techniques include analyses such as decision trees, neural networks, classifiers, and logistic regression.
Unsupervised learning occurs when an organization has data and wants to understand the relationship(s) between unlike data points. For example, if a retailer wants to sympathize purchasing patterns of its customers, an unsupervised learning model can be adult to find out which products are most oft purchased together or how to group their customers by purchase history. Is it called "unsupervised" learning considering no specific consequence is expected. Unsupervised learning techniques include clustering and association rules.
Privacy Concerns
The increasing power of data mining has caused concerns for many, especially in the area of privacy. In today'south digital world, it is becoming easier than ever to take information from disparate sources and combine them to do new forms of analysis. In fact, a whole industry has sprung up around this technology: data brokers. These firms combine publicly accessible data with data obtained from the authorities and other sources to create vast warehouses of data almost people and companies that they can then sell. This subject area will be covered in much more than detail in chapter 12 – the chapter on the ethical concerns of information systems.
Sidebar: What is data science? What is information analytics?
The term "data science" is a popular term meant to describe the analysis of large data sets to find new knowledge. For the by several years, it has been considered ane of the best career fields to go into due to its explosive growth and high salaries. While a data scientist does many different things, their focus is generally on analyzing large data sets using various programming methods and software tools to create new noesis for their arrangement. Data scientists are skilled in automobile learning and data visualization techniques. The field of data science is constantly changing, and information scientists are on the cutting edge of work in areas such as artificial intelligence and neural networks.
Knowledge Management
We end the chapter with a discussion on the concept of knowledge management (KM). All companies accrue cognition over the course of their existence. Some of this knowledge is written downwards or saved, merely not in an organized manner. Much of this knowledge is not written down; instead, it is stored within the heads of its employees. Knowledge management is the process of creating, formalizing the capture, indexing, storing, and sharing of the company'south knowledge in order to benefit from the experiences and insights that the company has captured during its existence.
Summary
In this chapter, we learned virtually the role that data and databases play in the context of information systems. Information is made upward of facts of the world. If you process information in a detail context, and then y'all have information. Knowledge is gained when information is consumed and used for determination making. A database is an organized collection of related data. Relational databases are the nearly widely used type of database, where data is structured into tables and all tables must be related to each other through unique identifiers. A database direction arrangement (DBMS) is a software application that is used to create and manage databases, and can accept the class of a personal DBMS, used past one person, or an enterprise DBMS that can be used by multiple users. A information warehouse is a special form of database that takes data from other databases in an enterprise and organizes it for analysis. Data mining is the process of looking for patterns and relationships in big data sets. Many businesses use databases, data warehouses, and information-mining techniques in social club to produce business organization intelligence and gain a competitive advantage.
Study Questions
- What is the deviation between data, information, and knowledge?
- Explain in your own words how the information component relates to the hardware and software components of information systems.
- What is the difference between quantitative information and qualitative data? In what situations could the number 42 exist considered qualitative data?
- What are the characteristics of a relational database?
- When would using a personal DBMS make sense?
- What is the departure between a spreadsheet and a database? List iii differences betwixt them.
- Describe what the term normalization means.
- Why is information technology important to define the data type of a field when designing a relational database?
- Proper name a database you interact with oftentimes. What would some of the field names exist?
- What is metadata?
- Name three advantages of using a information warehouse.
- What is information mining?
- In your own words, explain the deviation between supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Give an example of each (not from the book).
Exercises
- Review the design of the Schoolhouse database earlier in this affiliate. Reviewing the lists of data types given, what data types would you assign to each of the fields in each of the tables. What lengths would y'all assign to the text fields?
- Download Apache OpenOffice.org and use the database tool to open the "Pupil Clubs.odb" file available here. Take some fourth dimension to learn how to modify the database structure and so see if you can add the required items to support the tracking of kinesthesia advisors, as described at the cease of the Normalization department in the chapter. Here is a link to the Getting Started documentation.
- Using Microsoft Access, download the database file of comprehensive baseball statistics from the website SeanLahman.com. (If you lot don't accept Microsoft Access, you can download an abridged version of the file hither that is compatible with Apache Open Office). Review the structure of the tables included in the database. Come with 3 different information-mining experiments you would like to try, and explain which fields in which tables would accept to be analyzed.
- Do some original research and find two examples of information mining. Summarize each example and then write about what the 2 examples have in common.
- Bear some independent enquiry on the process of business concern intelligence. Using at least two scholarly or practitioner sources, write a two-folio newspaper giving examples of how business intelligence is existence used.
- Conduct some independent research on the latest technologies existence used for cognition management. Using at to the lowest degree two scholarly or practitioner sources, write a ii-page paper giving examples of software applications or new technologies being used in this field.
Source: https://opentextbook.site/informationsystems2019/chapter/chapter-4-data-and-databases-update/
0 Response to "An Example of a Retailerã¢â‚¬â„¢s Regularly Reviewing Operations Is the _____"
Postar um comentário